I am currently a Ph.D. at South China University of Technology (SCUT), advised by Prof. Kui Jia. I received my bachelor degree from the same university (i.e. SCUT) in 2020, and expect to obtain my Ph.D. degree in 2025. I am currently an intern at Tencent AI Lab.
I mainly focus on 3D Computer Vision. My current research interests include Computer Graphics, 3D Semantic Learning and Reconstruction. Recently, I am working on Multi-View Reconstruction.
📝 Publications

LetsTalk: Latent Diffusion Transformer for Talking Video Synthesis
Haojie Zhang*, Zhihao Liang*, Ruibo Fu, Zhengqi Wen, Xuefei Liu, Chenxing Li, Jianhua Tao, Yaling Liang
- In this paper, we present LetsTalk (LatEnt Diffusion TranSformer for Talking Video Synthesis), a diffusion transformer that incorporates modular temporal and spatial attention mechanisms to merge multimodality and enhance spatial-temporal consistency. To handle multimodal conditions, we first summarize three fusion schemes, ranging from shallow to deep fusion compactness, and thoroughly explore their impact and applicability. Then we propose a suitable solution according to the modality differences of image, audio, and video generation. For portrait, we utilize a deep fusion scheme (Symbiotic Fusion) to ensure portrait consistency. For audio, we implement a shallow fusion scheme (Direct Fusion) to achieve audio-animation alignment while preserving diversity.
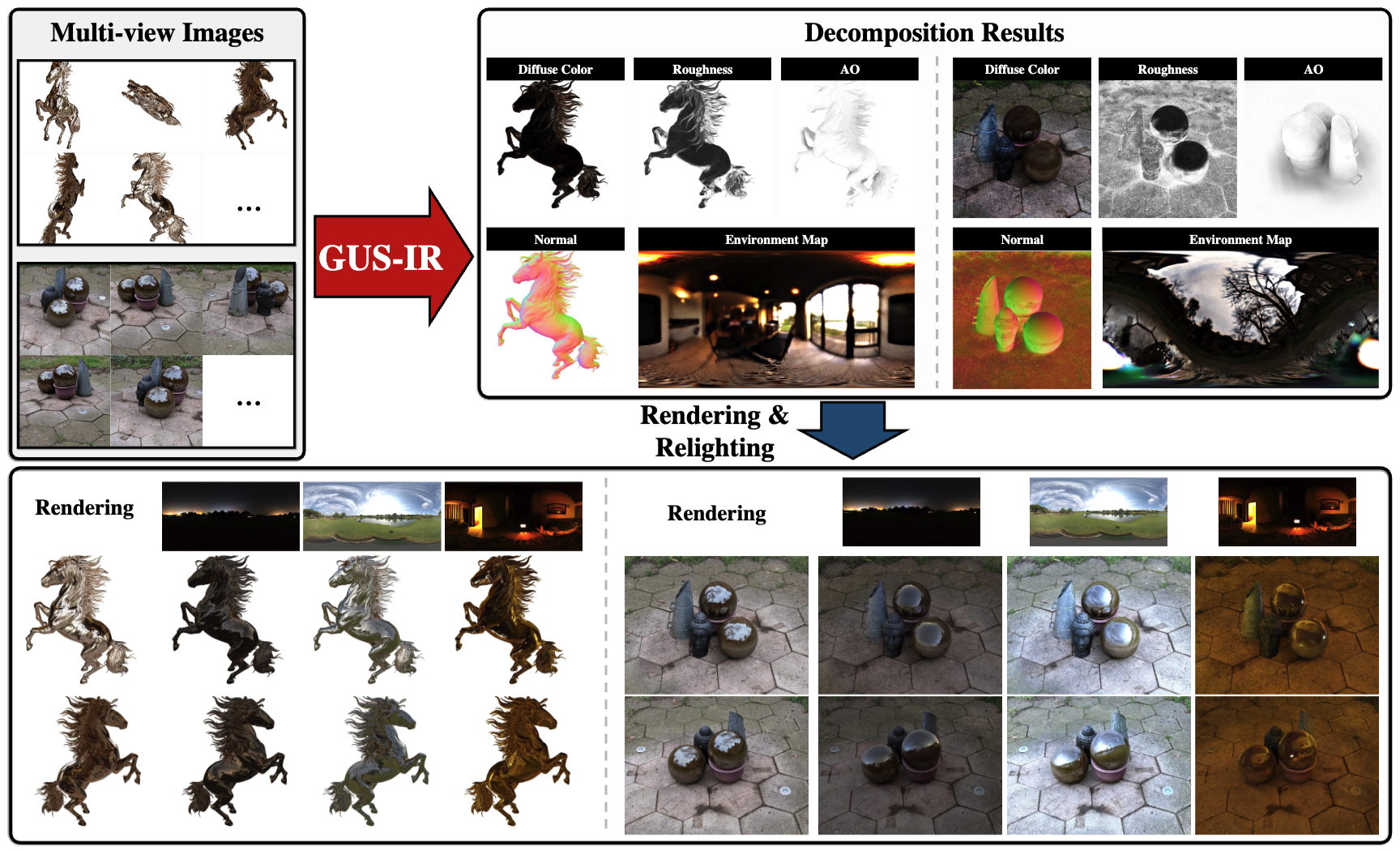
GUS-IR: Gaussian Splatting with Unified Shading for Inverse Rendering
Zhihao Liang, Hongdong Li, Kui Jia, Kailing Guo, Qi Zhang
- In this paper, we present GUS-IR, a novel framework designed to address the inverse rendering problem for complicated scenes featuring rough and glossy surfaces. This paper starts by analyzing and comparing two prominent shading techniques popularly used for inverse rendering, forward shading and deferred shading, effectiveness in handling complex materials. More importantly, we propose a unified shading solution that combines the advantages of both techniques for better decomposition. In addition, we analyze the normal modeling in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and utilize the shortest axis as normal for each particle in GUS-IR, along with a depth-related regularization, resulting in improved geometric representation and better shape reconstruction. Furthermore, we enhance the probe-based baking scheme proposed by GS-IR to achieve more accurate ambient occlusion modeling to better handle indirect illumination.
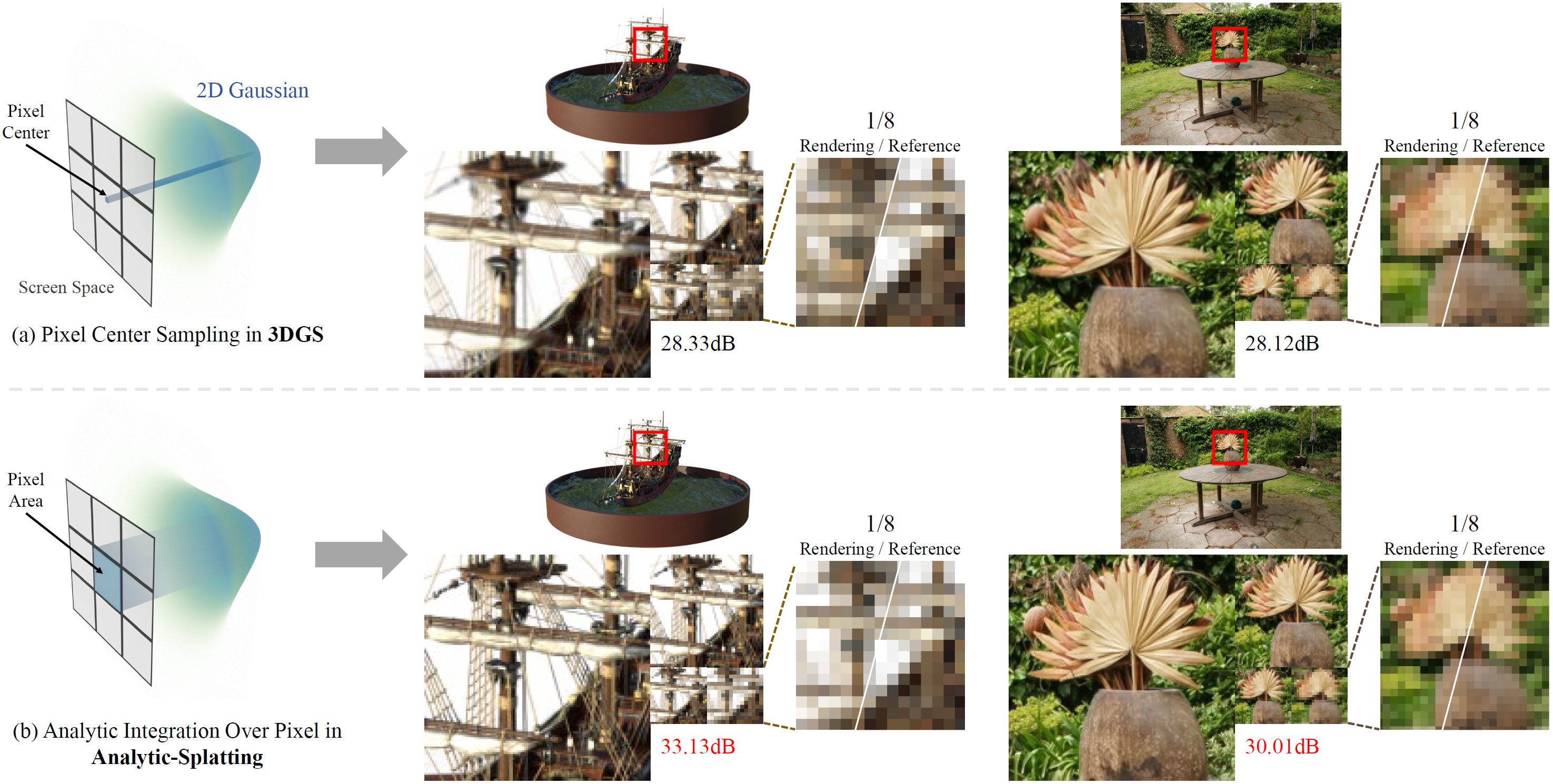
Analytic-Splatting: Anti-Aliased 3D Gaussian Splatting via Analytic Integration
Zhihao Liang, Qi Zhang, Wenbo Hu, Lei Zhu, Ying Feng, Kui Jia
- In this paper, we derive an analytical solution to address the aliasing caused by discrete sampling in 3DGS. More specifically, we use a conditioned logistic function as the analytic approximation of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) in a one-dimensional Gaussian signal and calculate the Gaussian integral by subtracting the CDFs. We then introduce this approximation in the two-dimensional pixel shading, and present Analytic-Splatting, which analytically approximates the Gaussian integral within the 2D-pixel window area to better capture the intensity response of each pixel. Moreover, we use the approximated response of the pixel window integral area to participate in the transmittance calculation of volume rendering, making Analytic-Splatting sensitive to the changes in pixel footprint at different resolutions.
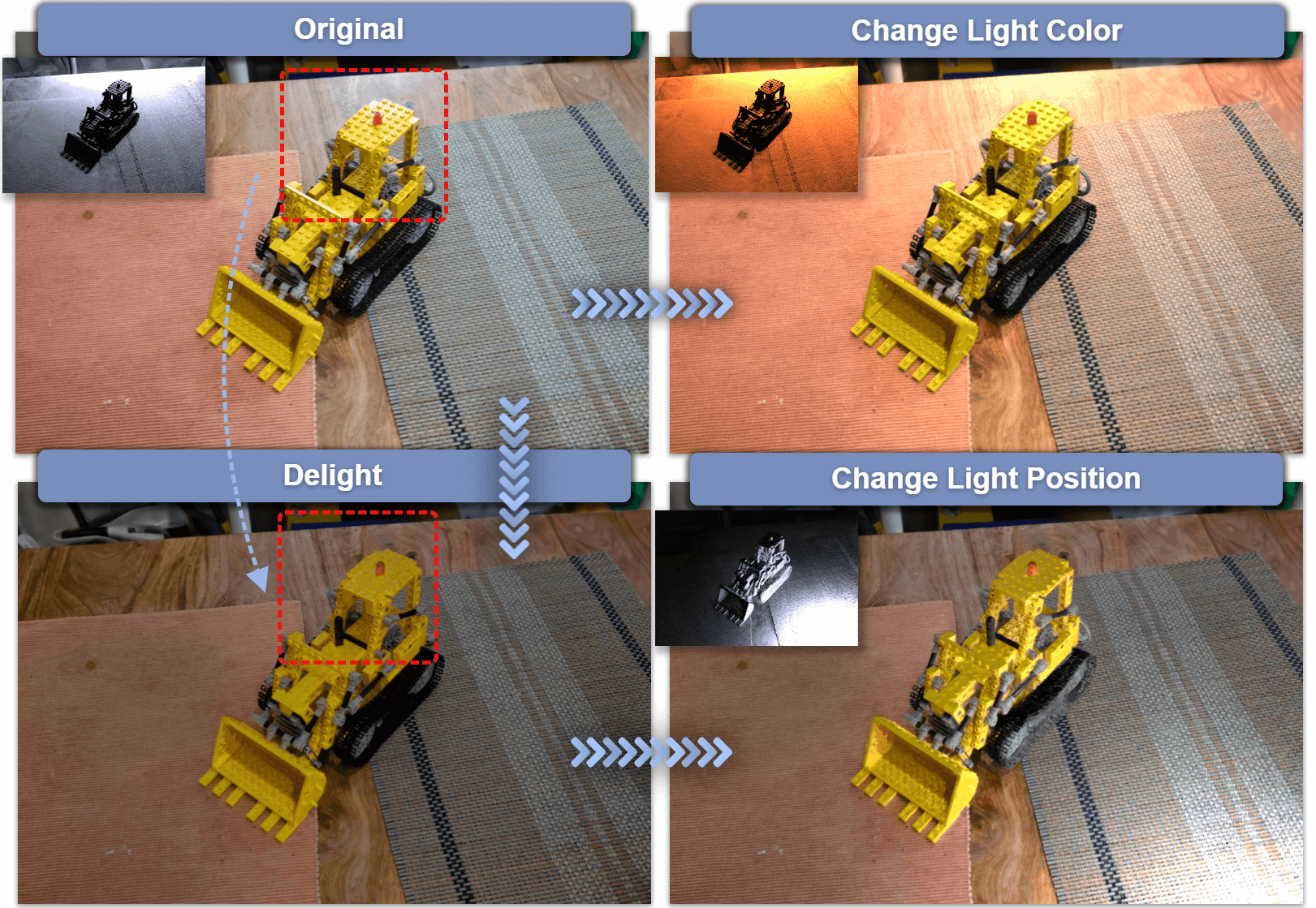
Kang Du, Zhihao Liang, Zeyu Wang
- We present GS-ID, a novel framework for illumination decomposition on Gaussian Splatting, achieving photorealistic novel view synthesis and intuitive light editing. In this work, we first introduce intrinsic diffusion priors to estimate the attributes for physically based rendering. Then we divide the illumination into environmental and direct components for joint optimization. Last, we employ deferred rendering to reduce the computational load. Our framework uses a learnable environment map and Spherical Gaussians (SGs) to represent light sources parametrically, therefore enabling controllable and photorealistic relighting on Gaussian Splatting.
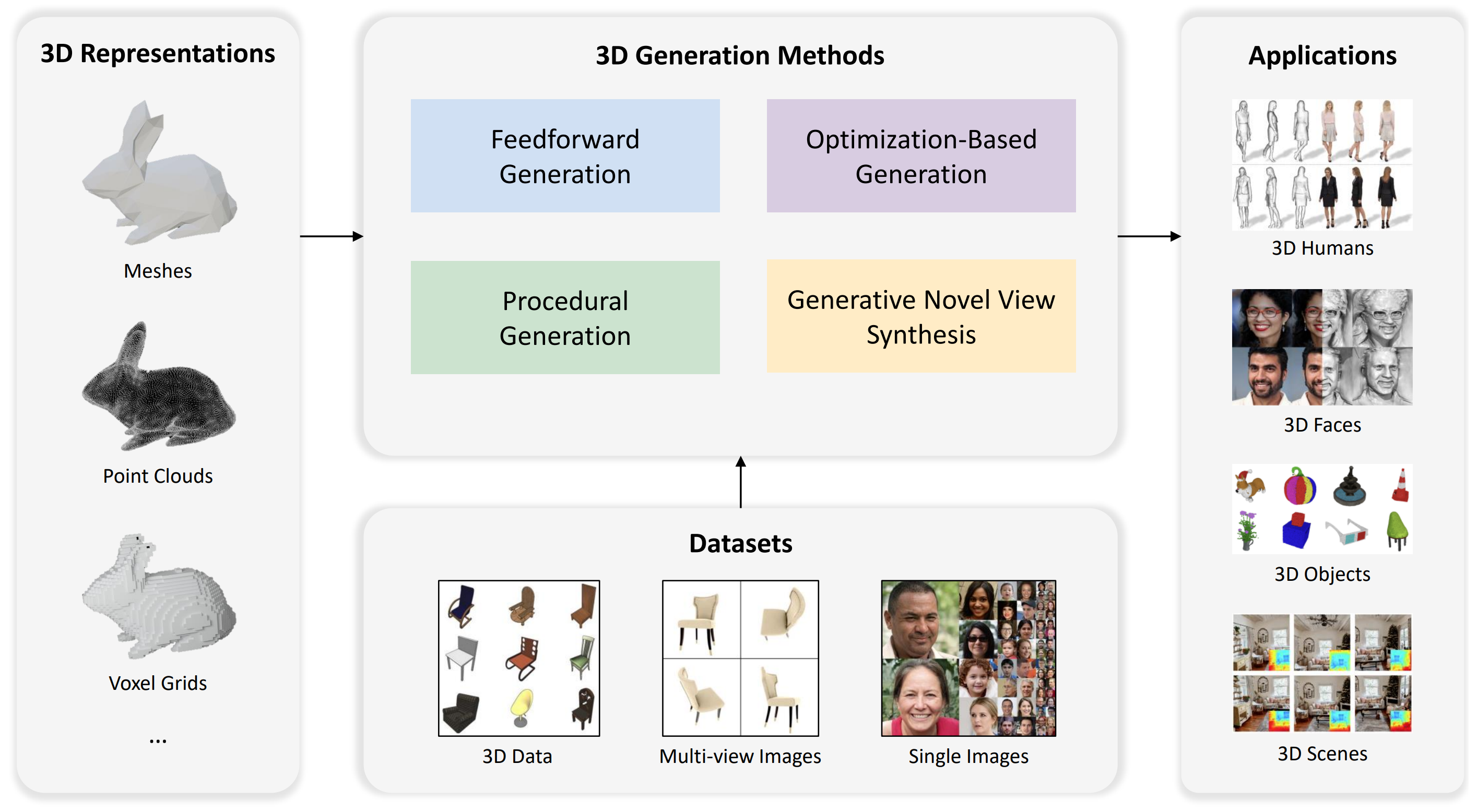
Advances in 3D Generation: A Survey
Xiaoyu Li, Qi Zhang, Di Kang, Weihao Cheng, Yiming Gao, Jingbo Zhang, Zhihao Liang, Jing Liao, Yan-Pei Cao, Ying Shan
- In this survey, we aim to introduce the fundamental methodologies of 3D generation methods and establish a structured roadmap, encompassing 3D representation, generation methods, datasets, and corresponding applications. We hope this survey will help readers explore this exciting topic and foster further advancements in the field of 3D content generation.
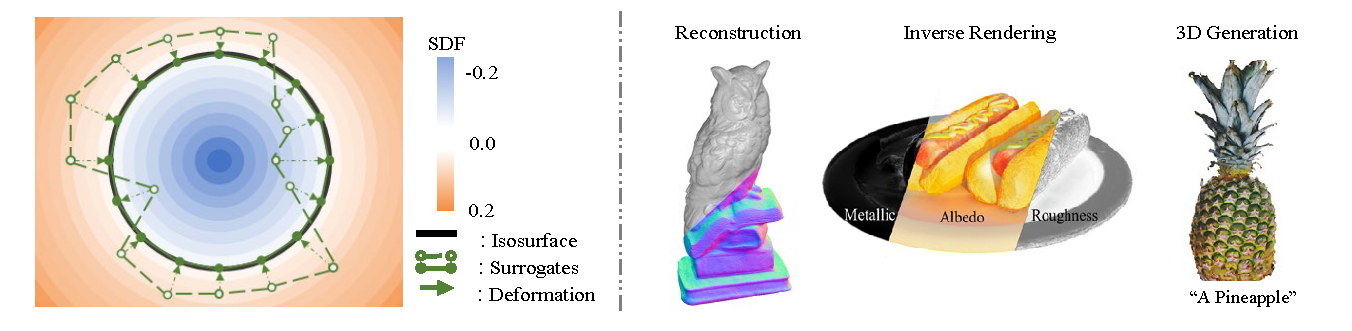
Zhangjin Huang*, Zhihao Liang*, Haojie Zhang, Yangkai Lin, Kui Jia
- We propose a new hybrid representation, termed Sur2f, that can enjoy the benefits of both explicit and implicit surface representations. This is achieved by learning two parallel streams of an implicit SDF and an explicit surrogate surface mesh, both of which, by rendering, receive supervision from multi-view image observations.
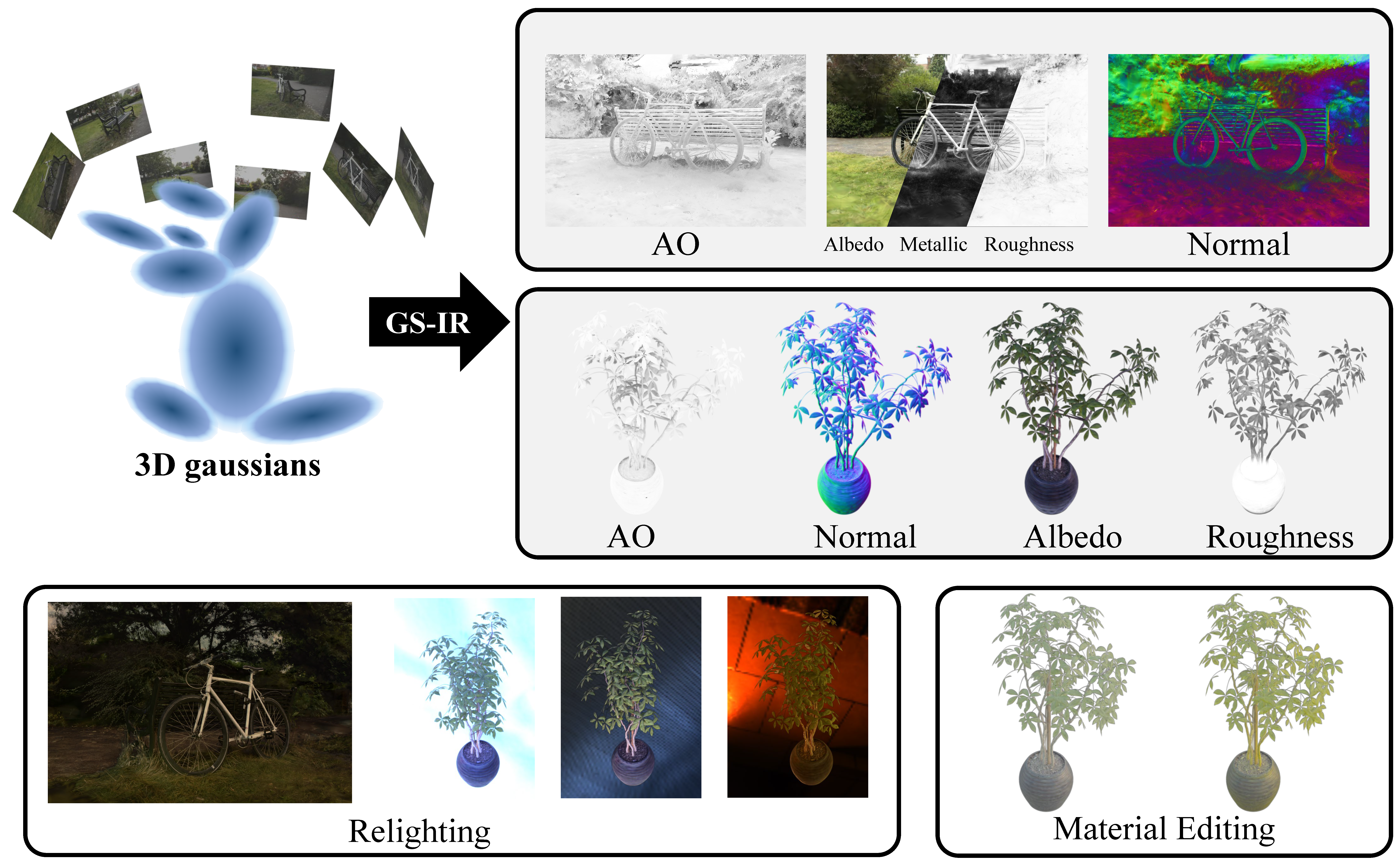
GS-IR: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering
Zhihao Liang*, Qi Zhang*, Ying Feng, Ying Shan, Kui Jia
- We present GS-IR that models a scene as a set of 3D Gaussians to achieve physically-based rendering and state-ofthe-art decomposition results for both objects and scenes.
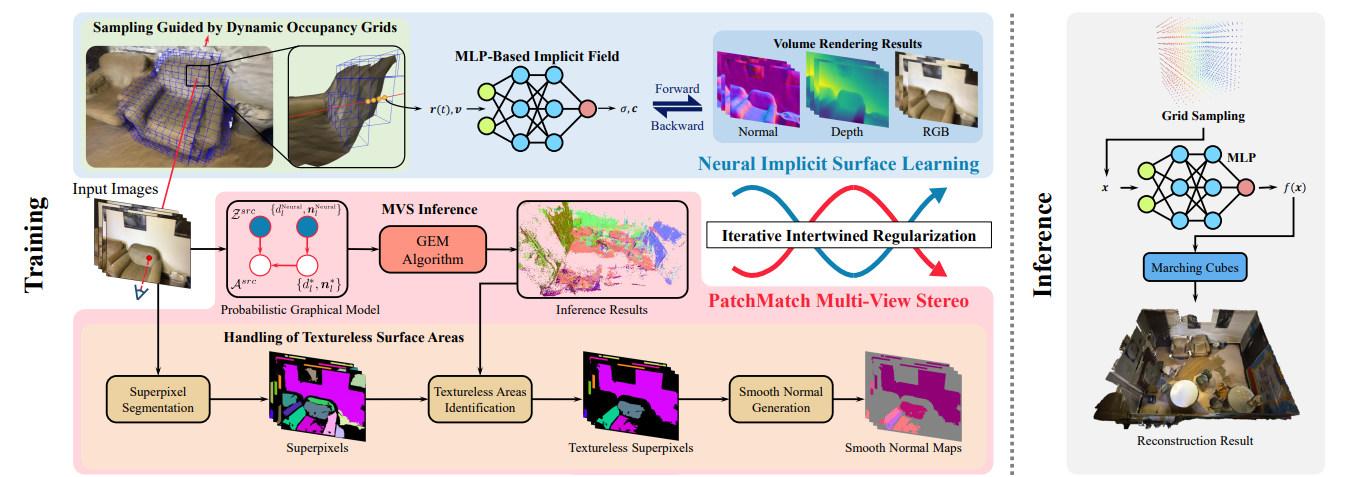
Zhihao Liang*, Zhangjin Huang*, Changxing Ding, Kui Jia
- We present a novel method of HelixSurf for reconstruction of indoor scene surface from multi-view images. HelixSurf enjoys the complementary benefits of the traditional MVS and the recent neural implicit surface learning, by regularizing the learning/optimization of one strategy iteratively using the intermediate prediction from the other.
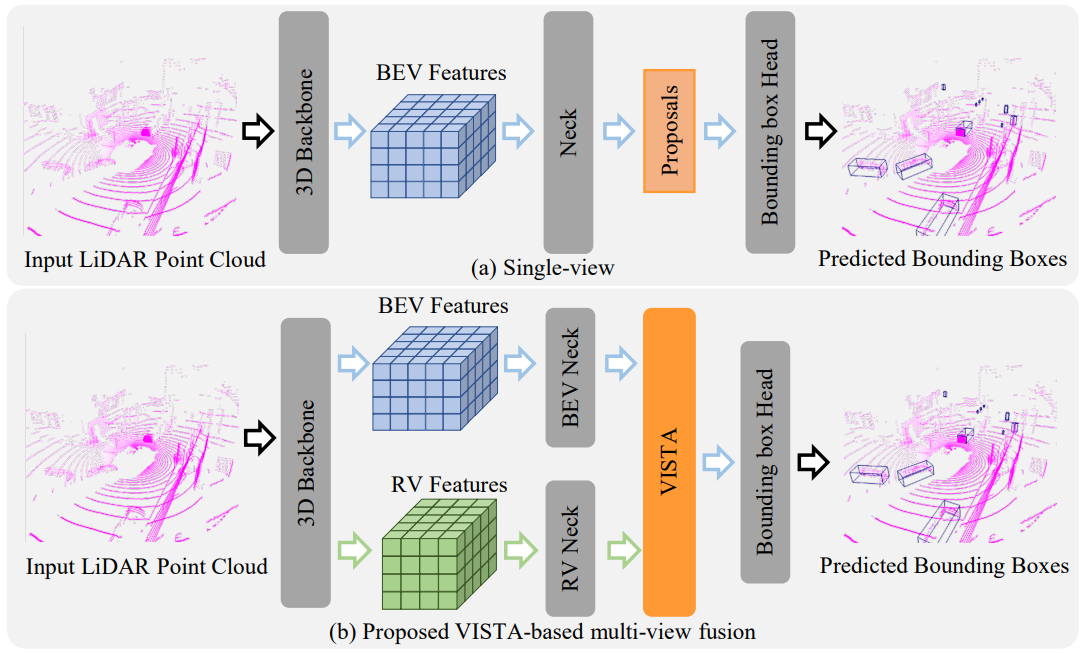
VISTA: Boosting 3D Object Detection via Dual Cross-VIew SpaTial Attention
Shengheng Deng*, Zhihao Liang*, Lin Sun, Kui Jia
- We propose a novel plug-and-play fusion module Dual Cross-VIew SpaTial Attention (VISTA) to produce well-fused multi-view features to boost the performances of 3D object detector. Our proposed VISTA replaces the MLPs with convolutional operators, which is capable of better handling the local cues for attention modeling.
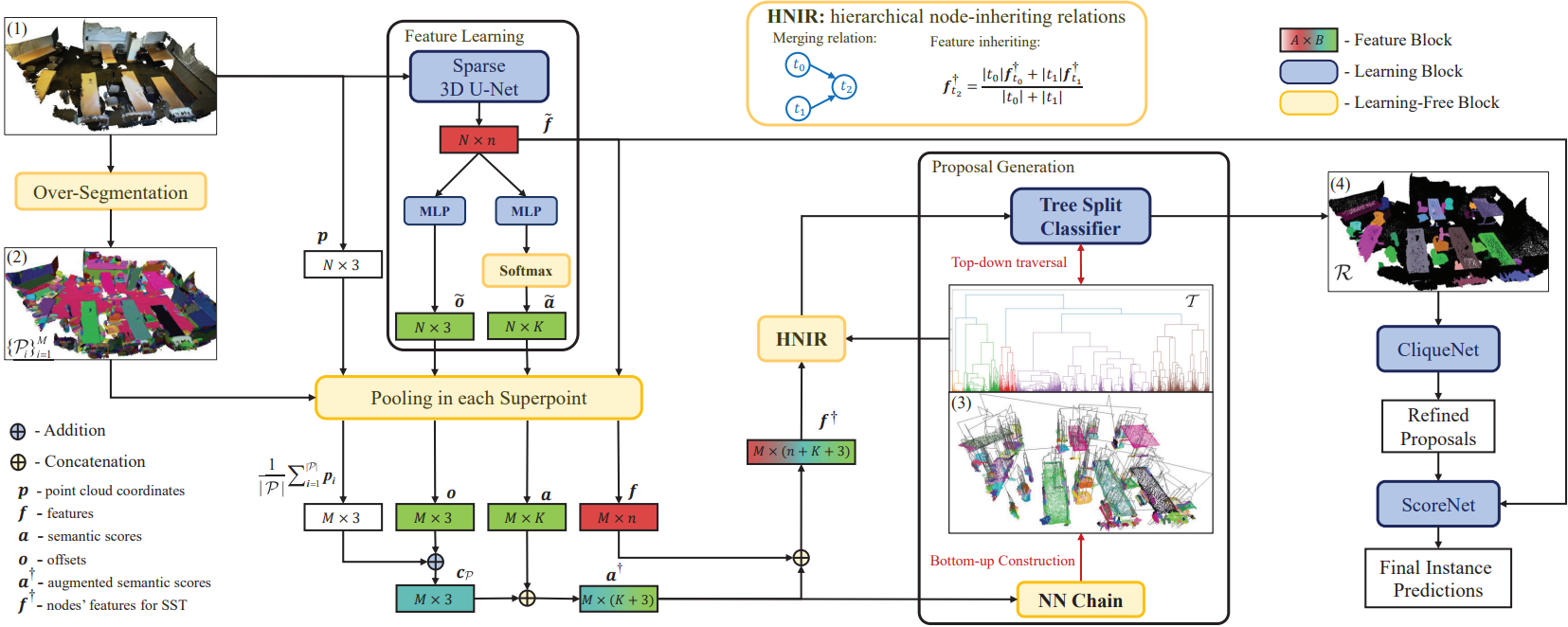
Instance Segmentation in 3D Scenes using Semantic Superpoint Tree Networks
Zhihao Liang, Zhihao Li, Songcen Xu, Mingkui Tan, Kui Jia
- We propose an end-to-end solution of Semantic Superpoint Tree Network (SSTNet) to directly propose and evaluate object instances from observed 3D scenes. By working with superpoints, our method enjoys the benefit of geometric regularity that supports consistent and sharp segmentations, especially at object boundaries.
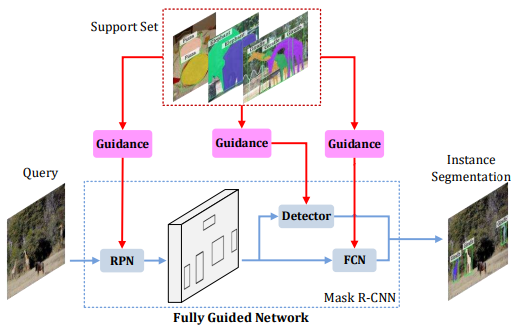
Fgn: Fully guided network for few-shot instance segmentation
Zhibo Fan, Jin-Gang Yu, Zhihao Liang, Jiarong Ou, Changxin Gao, Gui-Song Xia, Yuanqing Li
- We propose the Fully Guided Network, a novel framework for few-shot instance segmentation.
📖 Educations
- 2021.09 - Present, Ph.D., South China University of Technology, Guangzhou.
- 2020.09 - 2021.04, Master, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou.
- 2016.09 - 2020.06, Undergraduate, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou.
