Abstract
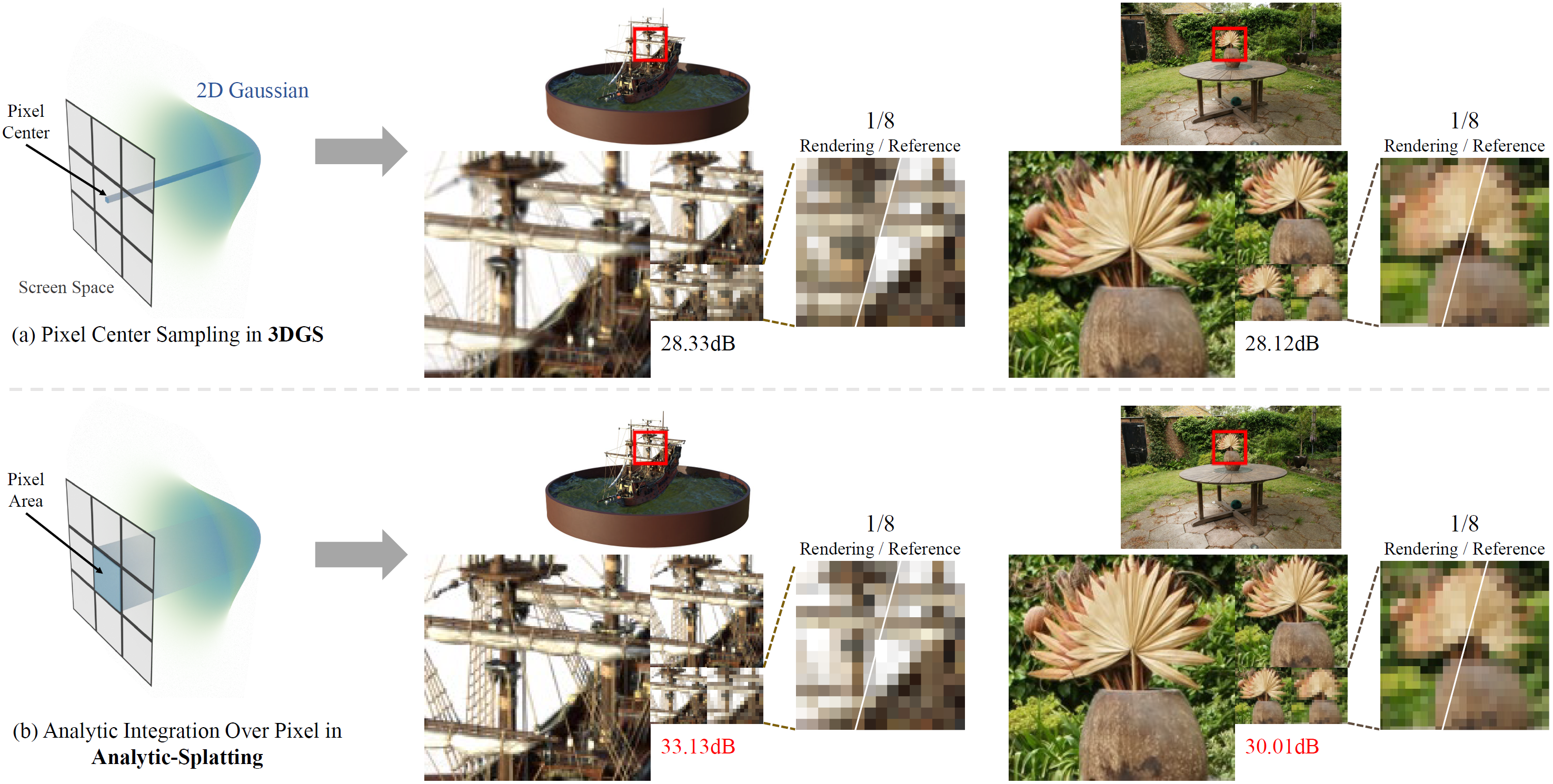
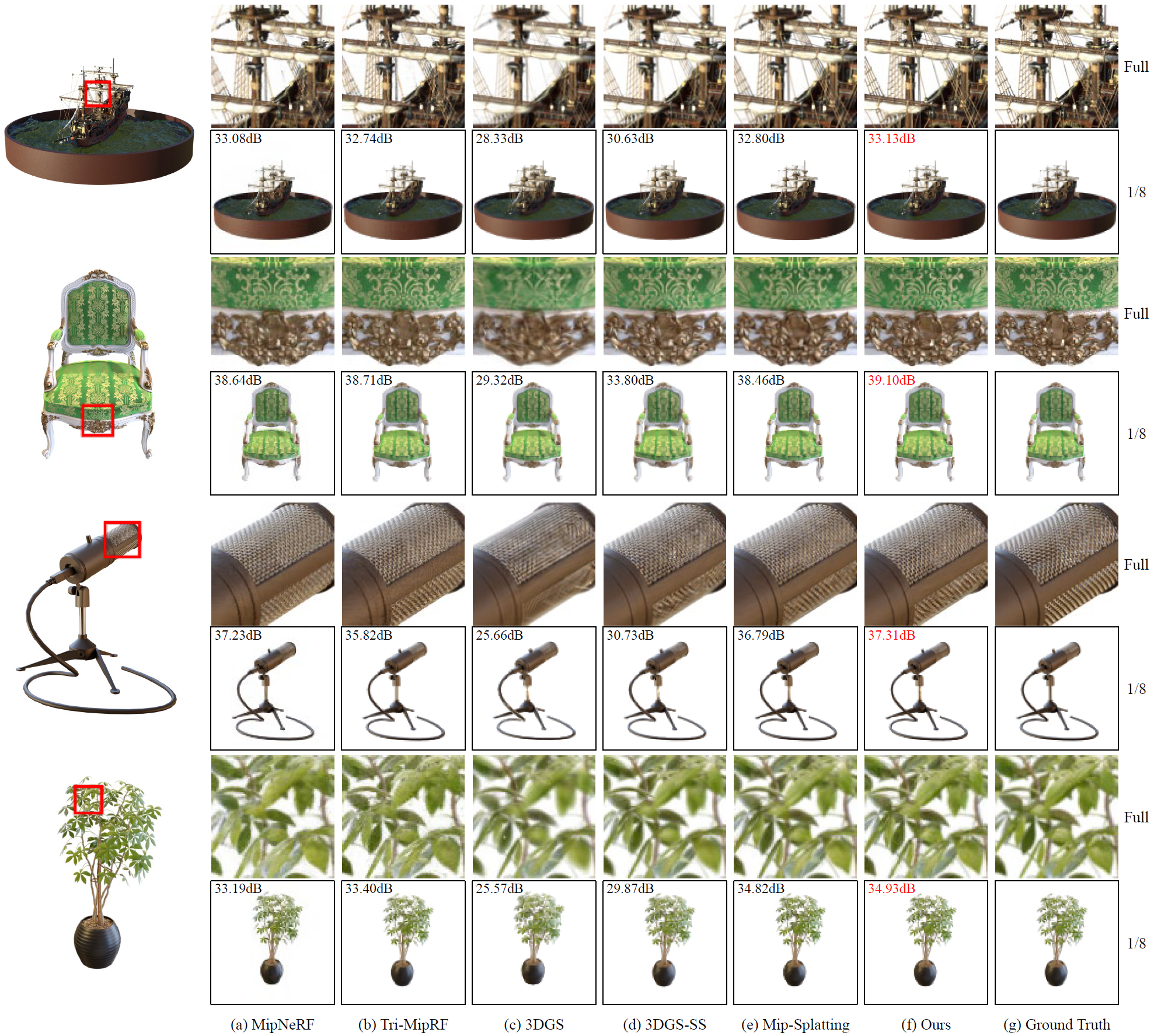
The 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) gained its popularity recently by combining the advantages of both primitive-based and volumetric 3D representations, resulting in improved quality and efficiency for 3D scene rendering. However, 3DGS is not alias-free, and its rendering at varying resolutions could produce severe blurring or jaggies. This is because 3DGS treats each pixel as an isolated, single point rather than as an area, causing insensitivity to changes in the footprints of pixels. Consequently, this discrete sampling scheme inevitably results in aliasing, owing to the restricted sampling bandwidth. In this paper, we derive an analytical solution to address this issue. More specifically, we use a conditioned logistic function as the analytic approximation of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) in a one-dimensional Gaussian signal and calculate the Gaussian integral by subtracting the CDFs. We then introduce this approximation in the two-dimensional pixel shading, and present Analytic-Splatting, which analytically approximates the Gaussian integral within the 2D-pixel window area to better capture the intensity response of each pixel. Moreover, we use the approximated response of the pixel window integral area to participate in the transmittance calculation of volume rendering, making Analytic-Splatting sensitive to the changes in pixel footprint at different resolutions. Experiments on various datasets validate that our approach has better anti-aliasing capability that gives more details and better fidelity.
Implementation
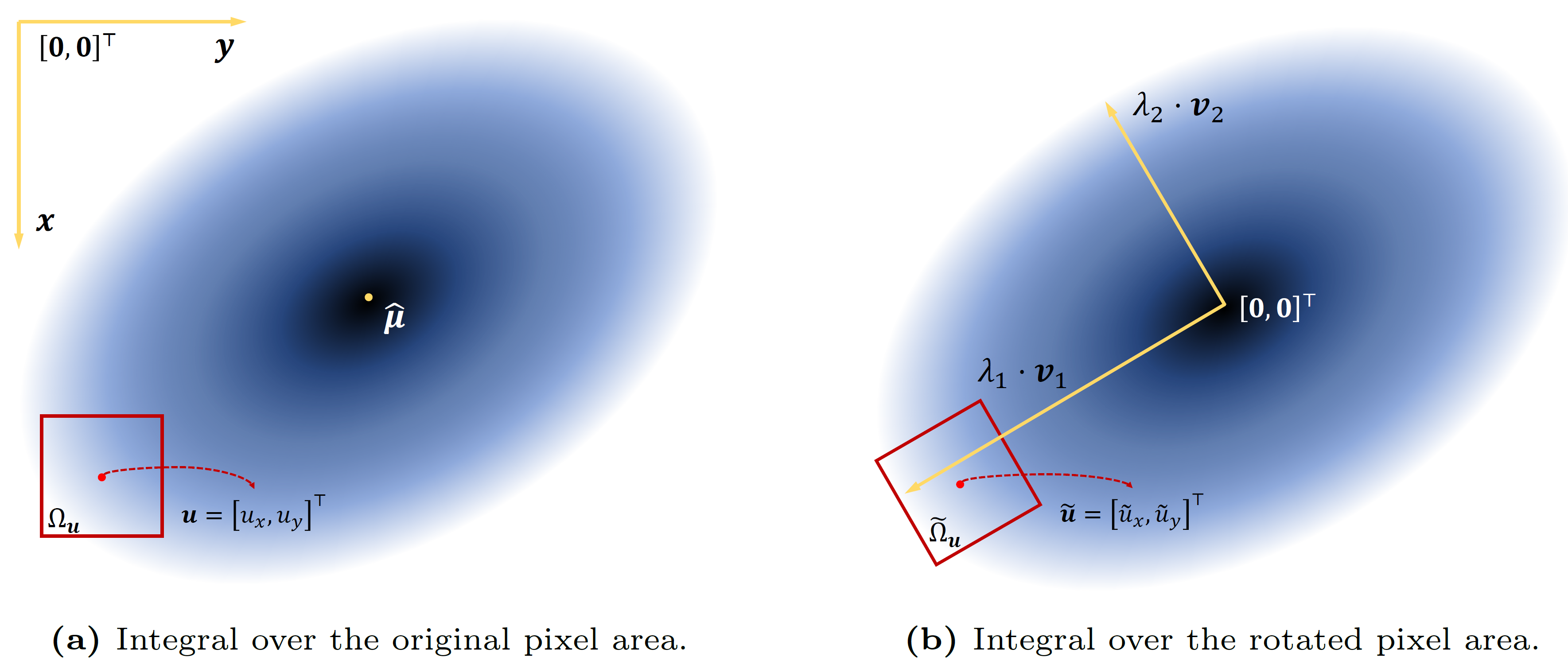
We diagonalize the 2D covariance matrix and slightly rotate the integration domain to resolve the difficult 2D correlated Gaussian integral into the multiplication of two independent 1D Gaussian integrals. The animation shows the integration domain of the same pixel area with different covariance (mainly reflected in the difference in eigenvectors). The animation is driven by Blender.